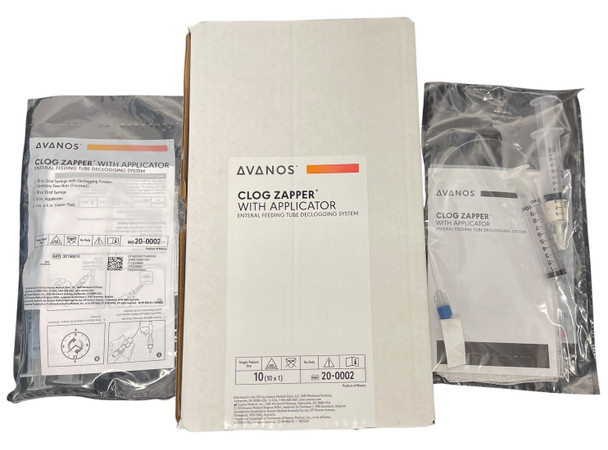
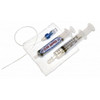
Our patented CLOG ZAPPER is a pre-mixed, pre-measured, pre-loaded system designed to break up formula clogs in enteral feeding devices.
CLOG ZAPPER combines an “enzyme cocktail,” acids, buffers, antimicrobial agents, and metal inhibitors in an all-inclusive, ready-to-use system. The ingredients all work together to loosen, break down and dislodge clogs. In clinical usage, CLOG ZAPPER was successful in restoring patency to feeding tubes clogged with enteral formulas over 75% of the time.